What Are The Different Dental Cavity Stages And How to Prevent Them?
Are you wondering why your child complains about a tiny toothache? Or why does food always seem to get stuck between their teeth?
What if the chalky spot your child ignored turns out to be a bigger concern? A cavity may progress slowly, but once developed, the dental cavity stages cannot be stopped from progressing with proper treatment. They often appear first without obvious pain, but their effects can be long-lasting: from irreversible decay to missed school days or more complicated dental treatments.
Understanding the stages of dental cavities is more than just knowing what happens to teeth, and what your child needs: a dental cavity filler, or beyond that.
It’s about spotting early warning signs, preventing unnecessary pain, and helping your child maintain a healthy, confident smile. If your child is experiencing it, it is worth visiting Next Level Pediatric Dentistry for a comprehensive dental exam for cavity fillings and sealants.
This guide outlines each stage of cavity development: from initial demineralization to serious abscess formation. We have also compiled some practical tips for prevention and care that you can start at home today.
Why Is Tooth Decay A Serious Oral Health Concern?
Tooth decay is a very common dental condition in both adults and children. It generally affects people of all age groups, but children are more susceptible to developing it.
How does it begin? With a smear of dental plaque, which is a sticky bacterial film, food particles, and saliva. The bacteria then feed on sugar in food and drink. If your child misses brushing, it is bacteria’s party day, and it eventually hardens into tartar, eroding the tooth enamel gradually.
The decaying process begins subtly, but it progresses through various stages, ultimately leading to tooth loss. And then you’ll have to opt for costly cosmetic fixes. People can often skip noticing its earliest stages, but regular oral hygiene maintenance can help prevent it for a lifetime.
Our primary aim at Next Level Pediatric Dentistry is to guide parents and children in maintaining oral hygiene through preventive care options, including daily brushing and flossing, using fluoride toothpaste, and chewing sugar-free gum. Habit formation is the first milestone for your children to avoid the need for expensive procedures, such as pulpotomy or pulpectomy.
Understanding Risk Factors for Tooth Decay
- Sugar and Diet: Consuming frequent sugary snacks feeds bacteria that produce acids, eroding enamel and increasing the risk of cavities. Limiting sugar helps protect developing teeth.
- Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva flow means less natural acid neutralization, raising the chance of decay and sensitivity. Staying hydrated and addressing causes is key.
- Genetics and Health Factors: For some children, genetics may contribute to the development of cavities due to weaker enamel or other health conditions that affect oral health.
- Frequent Snacking: Constant snacking keeps acids active on teeth. Allow breaks between meals so enamel can repair and prevent early decay.
- Inconsistent Dental Care: Skipping checkups and cleanings lets minor issues grow. Routine visits catch cavities early and maintain healthy teeth and gums.
Dental Cavity Stages - Elaborated For Parents
If your child is complaining of a persistent toothache, then it is worth noting the signs and symptoms of the extent of tooth decay. Given below are the stages of dental cavity progression:
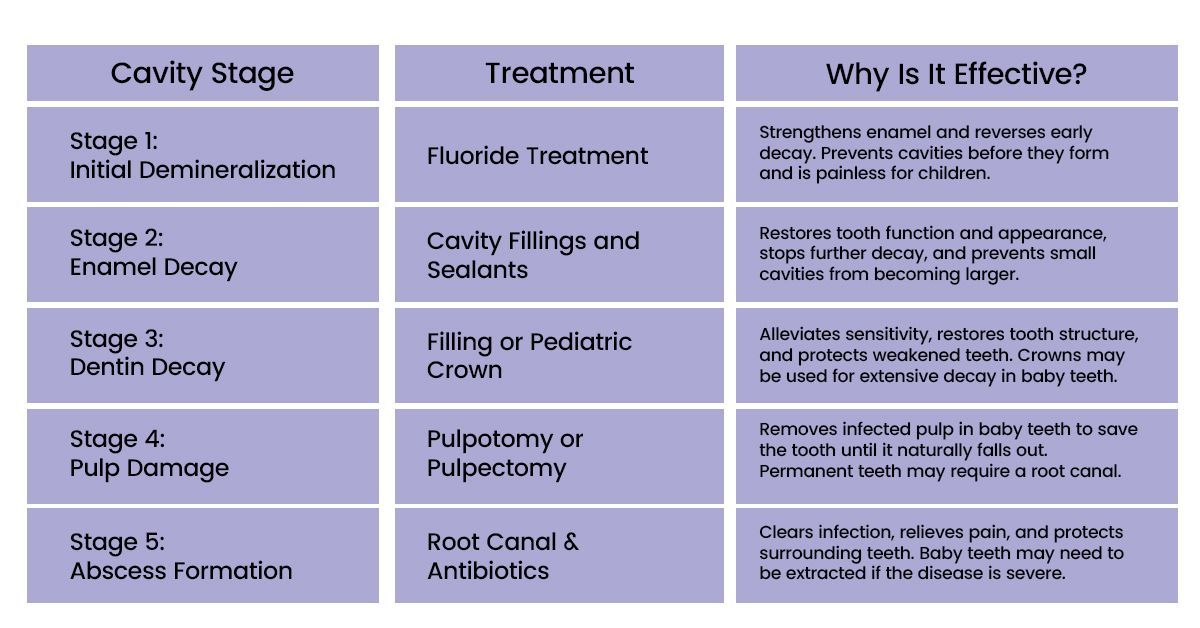
Stage 1: Initial Demineralization & Chalky Spots
The earliest stage of tooth decay is initial demineralization, often showing as tiny, white, chalky spots near the gum line. These subtle marks indicate minerals are leaching from enamel due to bacterial acids. At this stage, there’s usually no pain, making early detection crucial for preventing more serious issues later.
Fluoride treatments, whether administered at home or professionally, can remineralize enamel and help reverse early damage. Regular checkups enable pediatric dentists to identify these early signs and advise parents on proper brushing techniques, diet plan adjustments, and preventive care options to protect developing teeth.
Stage 2: Enamel Decay & Brown/Black Spots
Once decay progresses beyond demineralization, the enamel begins to break down. Small pits or brown and black spots appear on the tooth surface, signaling early cavities. This stage is often accelerated by frequent consumption of sugary snacks or drinks, which feed bacteria that produce enamel-eroding acids.
Treatment typically involves cavity fillings and sealants to restore tooth function and prevent further decay. For children, the fillings are designed to preserve baby teeth until they naturally fall out, while permanent teeth may require more durable materials. Early treatment keeps teeth healthy and prevents discomfort.
Stage 3: Dentin Decay & Increased Sensitivity to Hot/Cold Beverages
If decay reaches the dentin, the layer beneath the enamel, the teeth become more sensitive because dentin contains tiny tubes connecting to the nerves. Kids may complain about pain when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods, and persistent aches indicate decay is advancing.
Pediatric treatments often include fillings or, in more extensive cases, crowns for baby teeth to protect weakened teeth. Permanent teeth may need stronger fillings or protective restorations. Timely dental visits ensure pain is managed and decay doesn’t progress further.
Stage 4: Pulp Damage - Severe Decay
The decay reaching the pulp impacts nerves and blood vessels, causing pulpitis, an inflammation that may be reversible or irreversible. Symptoms include sharp or lingering pain, swelling, or pressure that makes chewing uncomfortable. Children’s baby teeth need special consideration because they guide permanent teeth.
For baby teeth, pediatric dentists may perform a pulpotomy (removing the affected pulp while preserving the rest) or pulpectomy (removing all pulp) to save the tooth until it naturally falls out. Adults and teenagers may require a root canal for their permanent teeth. Treating cavities early reduces the risk of infection and protects teeth from severe damage.
Stage 5: Abscess Formation With Serious Infections
If pulp damage is untreated, a tooth abscess can form, creating a pocket of pus at the root. Symptoms include throbbing tooth pain, swelling of the gums or jaw, and occasionally fever. Abscesses can spread infection to surrounding tissues if not treated promptly.
Pediatric treatment depends on the type of tooth. Baby teeth may require pulpectomy with antibiotics or extraction if severely infected. Permanent teeth often need a root canal plus antibiotics. Quick intervention protects your child’s oral health and ensures the infection doesn’t affect permanent teeth or overall well-being.
Practical Tips To Prevent Tooth Decay
Listed below are some practical tips for parents to keep their child’s teeth away from dental caries:
- Brush & floss daily: It removes plaque and food particles to reduce the risk of cavities.
- Use Fluoride toothpaste: It strengthens enamel and helps prevent tooth decay.
- Limit sugary & acidic foods: It protects enamel from demineralization.
- Eat nutrient-rich foods: Calcium and vitamins support strong teeth.
- Regular dental checkups: Early detection and professional cleanings prevent complicated dental problems.
How A Healthy Diet Protects Your Child’s Teeth?
Your child’s eating habits and diet play a big role in determining dental health. It is natural for kids to be attracted to junk food, chocolates, and sugary drinks.
Sugary foods and drinks feed cavity-causing bacteria, increasing the risk of tooth decay. Limiting sweets and acidic beverages, such as fruit juice, can help protect enamel and prevent cavities.
For young children, avoiding sugar-sweetened beverages is especially important. WHO recommends that kids under the age of two should avoid sugary drinks. Parents should encourage them to eat nutrient-rich foods like fruits, dairy products, and vegetables, even if kids detest onions and broccoli. Chewing sugar-free gum after meals can also boost saliva flow, neutralize acids, and support overall oral health.
Stage-Wise Treatment Options For Cavities
Advanced Dental Cavity Treatment At Next Level Pediatric Dentistry
When tooth decay reaches the deeper layers of a child’s tooth, more advanced care may be needed. If the pulp is affected, pulp therapy or a pediatric root canal may be necessary. Dental cavity treatments remove infected tissue, clean the tooth, and seal it, relieving pain while saving the baby or permanent tooth.
For teeth that are weakened or have lost significant portions, a pediatric dental crown can restore the tooth's strength, shape, and function. In rare cases where a tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be required to protect surrounding teeth and gums. After extraction, options such as space maintainers help preserve alignment until the permanent teeth emerge. Prompt care and regular pediatric dental visits prevent advanced decay and ensure healthy, lasting smiles.
Dentist-Recommended Way Of Sealing Off Cavities
Don’t Miss Your Regular Dental Appointments To Stop Dental Cavity Stages From Progressing!
You should regularly check with your dentist to catch the onset of cavities before they develop into tooth decay, which can potentially lead to tooth loss. Visit Next Level Pediatric Dentistry to keep your child’s smile healthy and prevent future dental problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How serious is a small dental cavity?
Even small cavities can grow, cause pain, or lead to infection. Early treatment helps keep teeth healthy and prevents more serious problems. - What is the first sign of tooth decay?
White, chalky spots on teeth indicate early enamel loss and suggest the progression of dental cavity stages. - How can I prevent tooth decay?
Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, floss, limit sugary foods, and schedule regular dental checkups. - What are the treatment options for enamel decay?
Fillings restore the tooth. Fluoride treatment can help prevent early spots. Advanced cases may need crowns or pulp therapy. - Why are regular dental checkups important?
Checkups can even catch a small dental cavity early, clean teeth professionally, and guide parents on healthy habits.